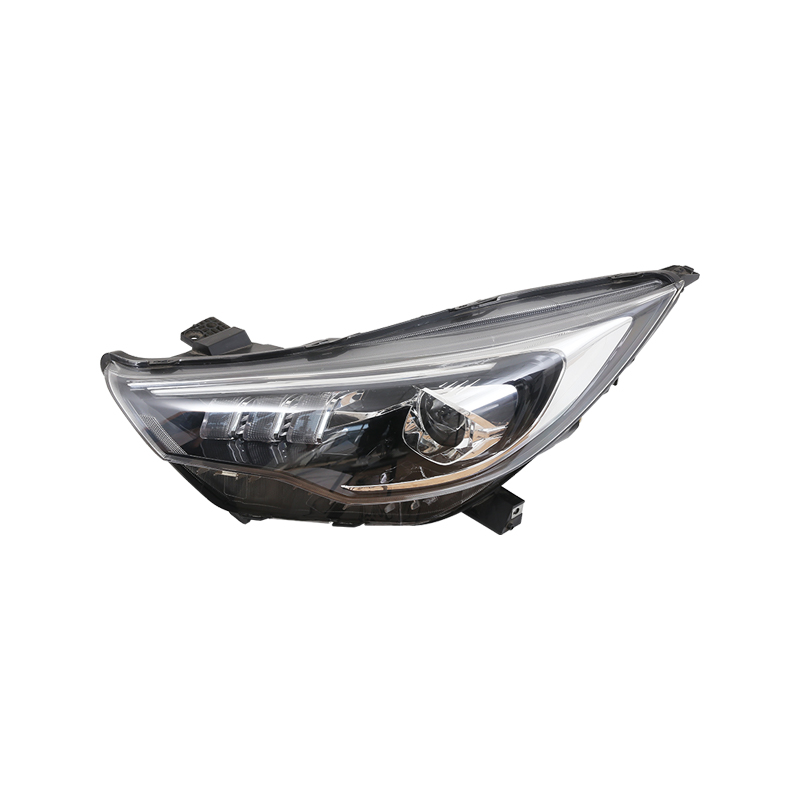
In the realm of automotive manufacturing, the production of auto headlight base housing and the precision involved in plastic injection mold tooling are essential for creating durable, efficient, and visually appealing lighting components.
Auto Headlight Base Housing Molding
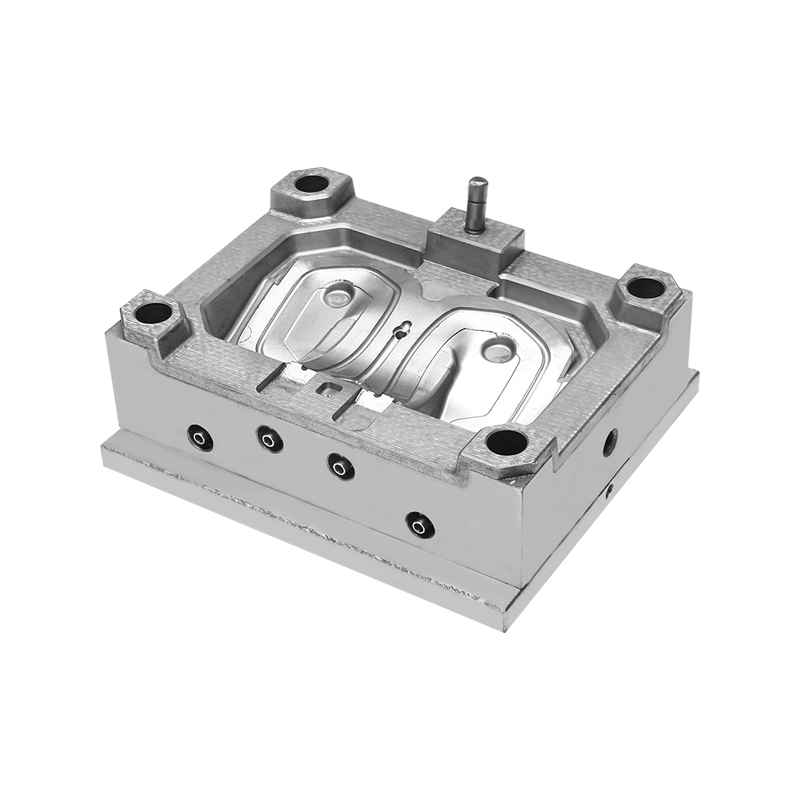
The auto headlight base housing molding process is integral to crafting the structural foundation of automotive headlight assemblies. This process involves several key steps to ensure the functionality and aesthetic quality of the final product:
Design and Engineering: The process begins with meticulous design and engineering of the auto headlight base housing. Designers utilize advanced CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software to create detailed 3D models that define the geometry, dimensions, and functional features of the housing. Factors such as light distribution, heat dissipation, and integration with electrical components are carefully considered during this phase.
Material Selection: Selecting the appropriate material is critical for the auto headlight base housing. Common materials include high-performance plastics such as polycarbonate (PC) or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), chosen for their durability, impact resistance, and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. The material choice ensures that the housing meets regulatory requirements and enhances the longevity of the headlight assembly.
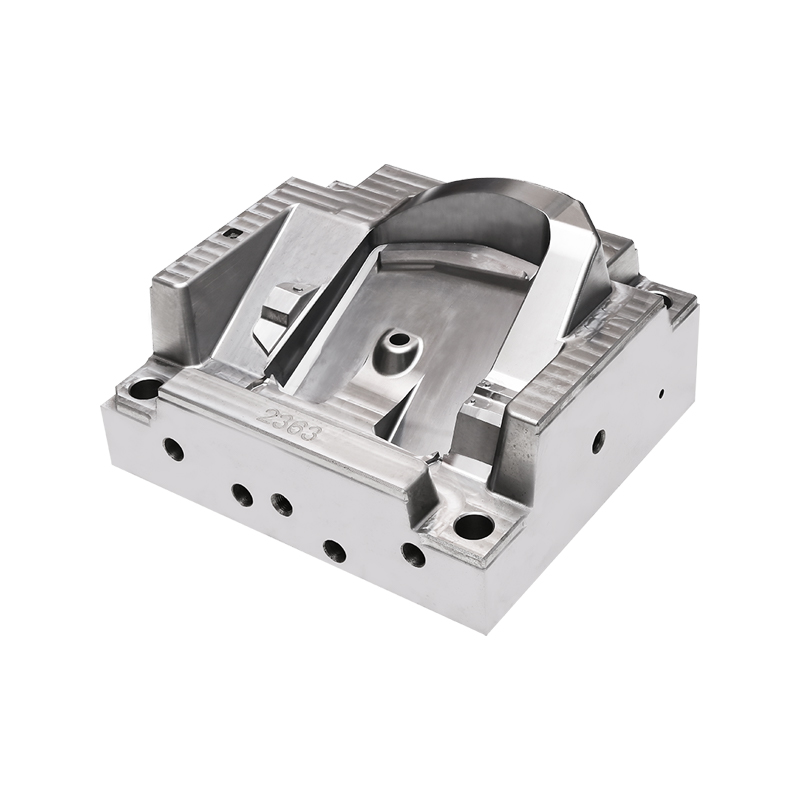
Mold Design and Fabrication: Once the design is finalized, the next step is mold design and fabrication. Injection molds are typically crafted from hardened steel or aluminum using precision machining techniques such as CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling and EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining). The mold consists of cavities, cores, runners, and gating systems that replicate the intricate details of the headlight base housing.
Injection Molding Process: During injection molding, the selected plastic resin is heated to a molten state and injected into the mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is held closed until the plastic material cools and solidifies, conforming to the shape of the mold cavity. Advanced injection molding machines ensure precise control over temperature, pressure, and cycle times, optimizing production efficiency and part quality.
Post-Molding Operations: After the plastic has solidified, the mold opens, and the auto headlight base housing is ejected from the mold cavity. Post-molding operations may include trimming excess material, surface finishing (e.g., polishing or texture application), and assembly of additional components such as lenses or bulb sockets. These operations ensure the housing meets dimensional accuracy and aesthetic requirements before final inspection.
Plastic Injection Mold Tooling
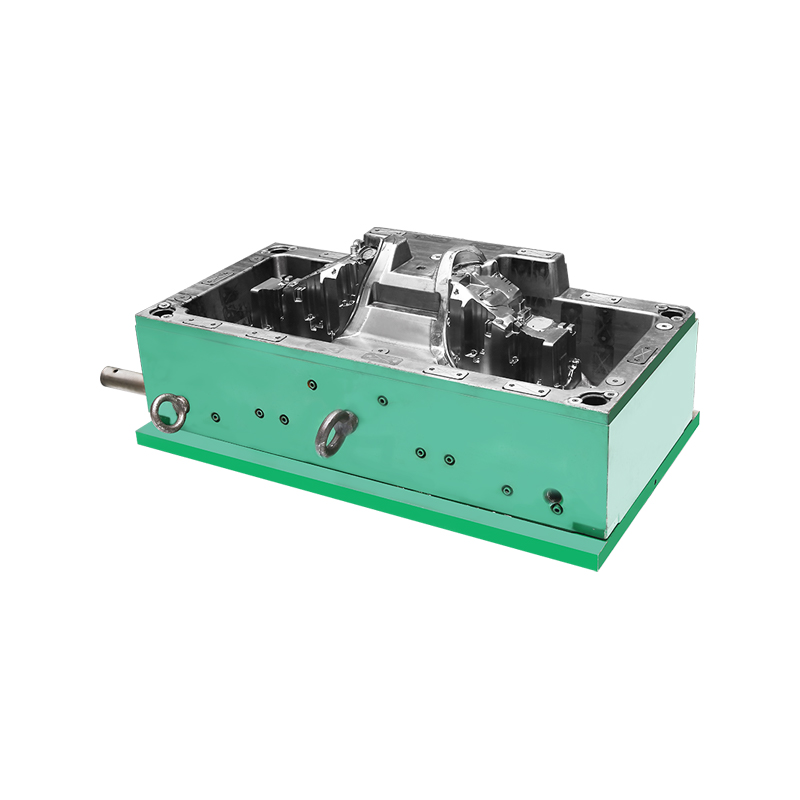
Plastic injection mold tooling is a foundational aspect of manufacturing processes across various industries, enabling the production of precise and complex plastic components. Here's an overview of the key considerations and processes involved in plastic injection mold tooling:
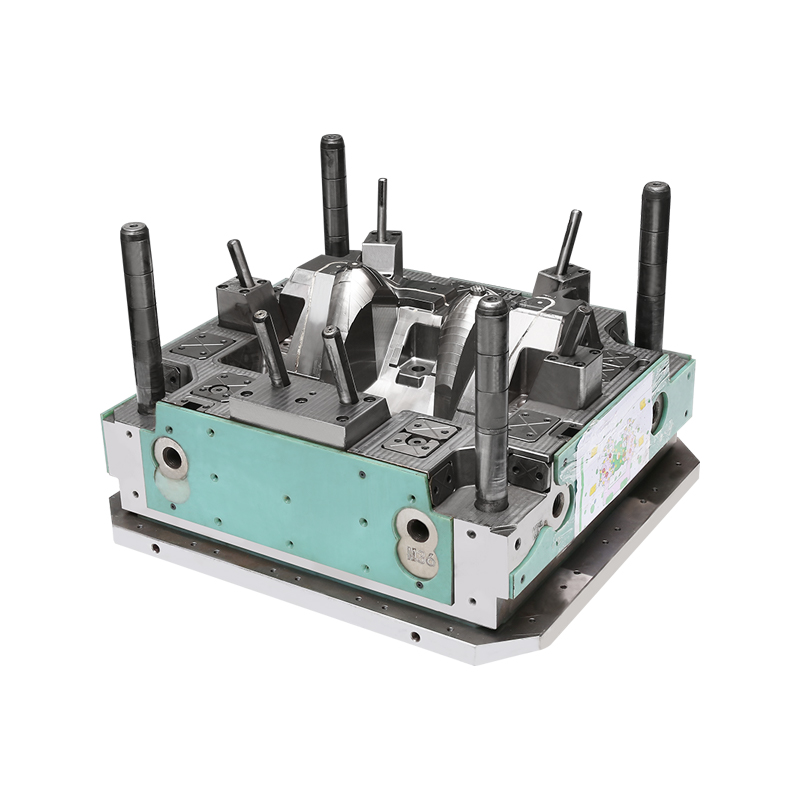
Tooling Design: The tooling design phase begins with the creation of detailed 3D CAD models based on product specifications. Tooling engineers design molds that include cavities, cores, ejector systems, runners, and gating systems. These components are crafted from high-quality materials such as hardened steel or aluminum alloys to withstand the high pressures and temperatures of injection molding.
Precision Machining: Precision machining techniques, including CNC milling and EDM, are employed to fabricate mold components to exacting tolerances. CNC machines use computer-controlled movements to achieve intricate details and precise geometries required for complex plastic parts. EDM utilizes electrical discharges to shape hardened steel components with precision.
Tooling Fabrication: Once the mold components are machined, they are assembled into a complete injection mold. Assembly involves integrating cooling channels, alignment features, and heating elements as required. The assembled mold undergoes rigorous testing to verify functionality, including mold open/close cycles, material flow simulations, and temperature control.
Injection Molding Integration: After successful testing, the injection mold is installed in an injection molding machine. The machine heats the plastic resin to a molten state and injects it into the mold cavity under high pressure. The mold is held closed until the plastic solidifies, forming the desired shape of the plastic part.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español








