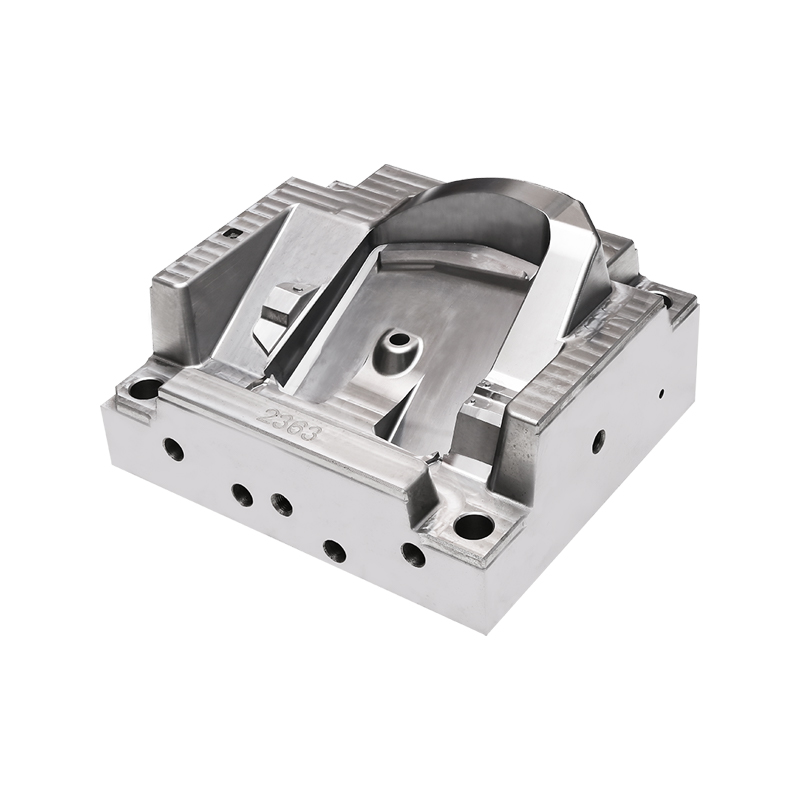
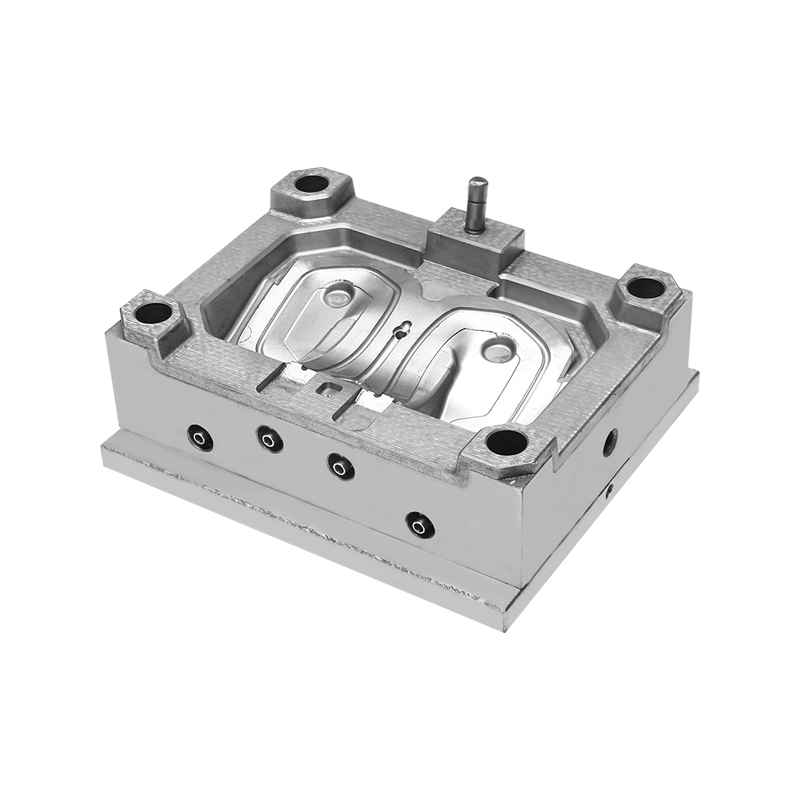
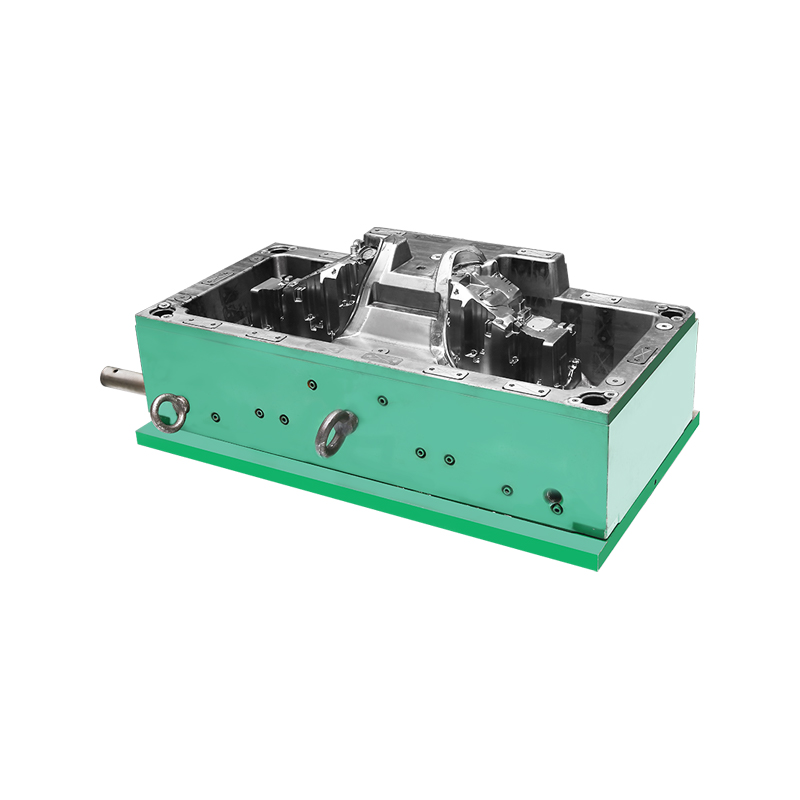
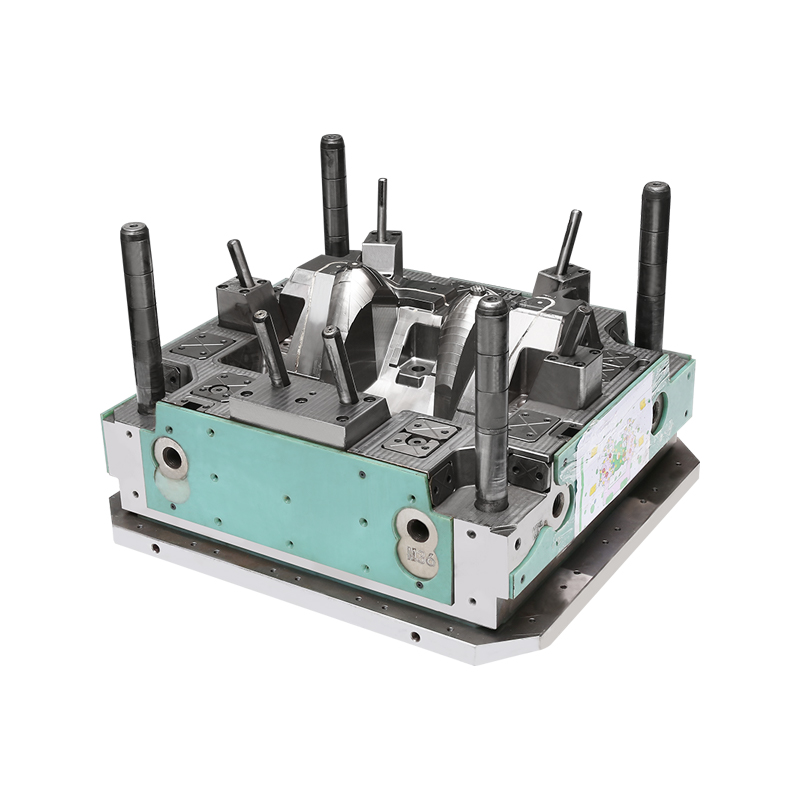
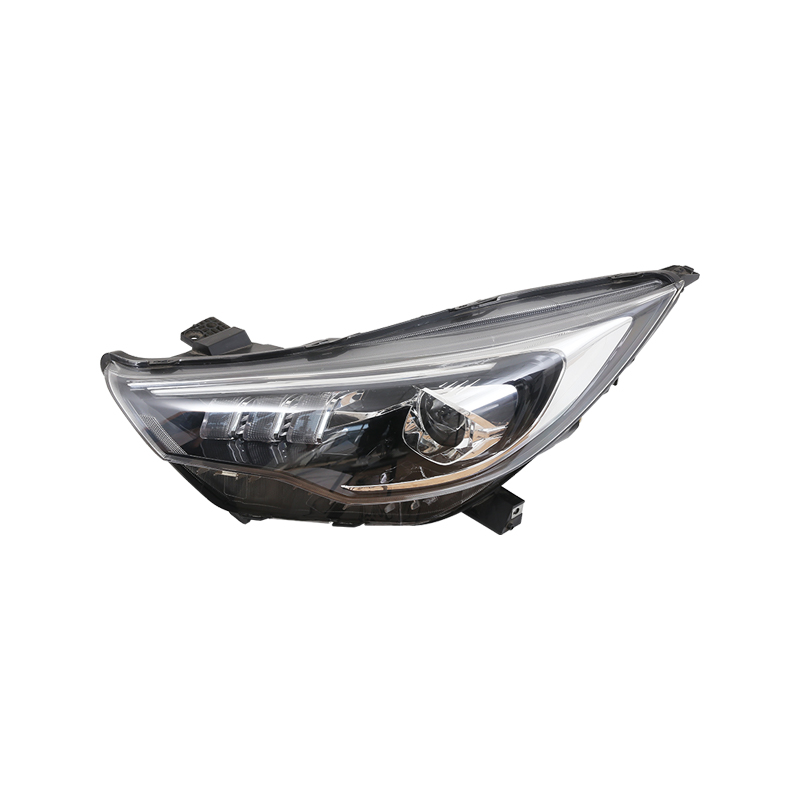
I. The Creation of Auto Lampshades Mould
The process of making auto lampshades mould is a testament to the precision and innovation in the automotive industry. These mould are not merely tools; they are the foundation of a vehicle's visual identity and safety features.
1.1. Design and Conceptualization
The journey of an auto lampshades mould begins with a design that is both aesthetically pleasing and functionally sound. Designers use CAD software to create a 3D model of the lampshade, taking into account the curvature, thickness, and material properties required for light distribution and structural integrity.
1.2. Material Selection
The choice of material is crucial. Polycarbonate, for instance, is often selected for its clarity, impact resistance, and heat resistance. The material must be able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the injection moulding process.
1.3. Tooling and Machining
Once the design is finalized, the tooling process begins. This involves creating a precise mould cavity that matches the design specifications. High-speed CNC machines are used to carve the mould from a solid block of steel, ensuring the accuracy of every detail.
1.4. Testing and Refinement
Before the mould is used for mass production, it undergoes rigorous testing. Prototypes are made to check for any imperfections or deviations from the design. Adjustments are made as necessary to ensure the mould meets the quality standards.
1.5. Mass Production
With the mould, the auto lampshades can now be produced in large quantities. The mould is loaded into an injection moulding machine, where the plastic material is melted and injected into the mould cavity. Once cooled and solidified, the lampshade is ejected, ready for assembly.
II. Definition and Working Principle of Precision Plastic Injection Moulding
Precision plastic injection moulding is a manufacturing process that allows for the production of complex, high-precision plastic parts with a high degree of repeatability and consistency.
2.1. Definition
Precision plastic injection moulding is defined as the process of injecting molten plastic material into a precisely machined mould cavity, where it cools and solidifies to take the shape of the cavity. This process is used to create a wide range of plastic components, from small intricate parts to large, structural components.
2.2. Working Principle
The working principle of precision plastic injection moulding involves several key steps:
2.2.1. Material Preparation
Plastic pellets or granules are fed into the hopper of the injection moulding machine. These pellets are then melted in the barrel of the machine, where they are heated and mixed to a uniform temperature and viscosity.
2.2.2. Injection
The molten plastic is then injected into the mould cavity under high pressure. The injection unit of the machine controls the speed, pressure, and volume of the plastic flow, ensuring that the mould is filled uniformly and without air traps.
2.2.3. Cooling and Solidification
Once the mould is filled, the plastic material cools and solidifies within the mould cavity. This cooling process is critical, as it determines the final shape, dimensions, and surface finish of the part.
2.2.4. Ejection
After the plastic has solidified, the mould opens, and the finished part is ejected from the mould cavity. The mould then closes, and the process begins anew for the next part.
2.2.5. Post-Processing
In some cases, the ejected part may require post-processing, such as trimming, painting, or assembly with other components.
2.3. Importance of Precision
Precision in plastic injection moulding is crucial for several reasons. It ensures that the final product meets the design specifications, has the required mechanical properties, and fits with other components in the assembly. Precision also reduce waste and rejects, bring about cost savings and increased efficiency.
 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский Español
Español








